- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2024-03-22 Origin: Site








Relay is an electrical controller that induces a step change in the controlled quantity in an electrical output circuit when the change in the input quantity (excitation quantity) meets specified requirements. It plays roles such as automatic regulation, safety protection, and circuit switching in circuits. By utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction, it controls the flow of large currents with small currents, thus achieving control and protection of the circuit. Relays are indispensable components in modern electrical control systems. Below is a detailed introduction to the principles, classifications, operating modes, and applications of relays.
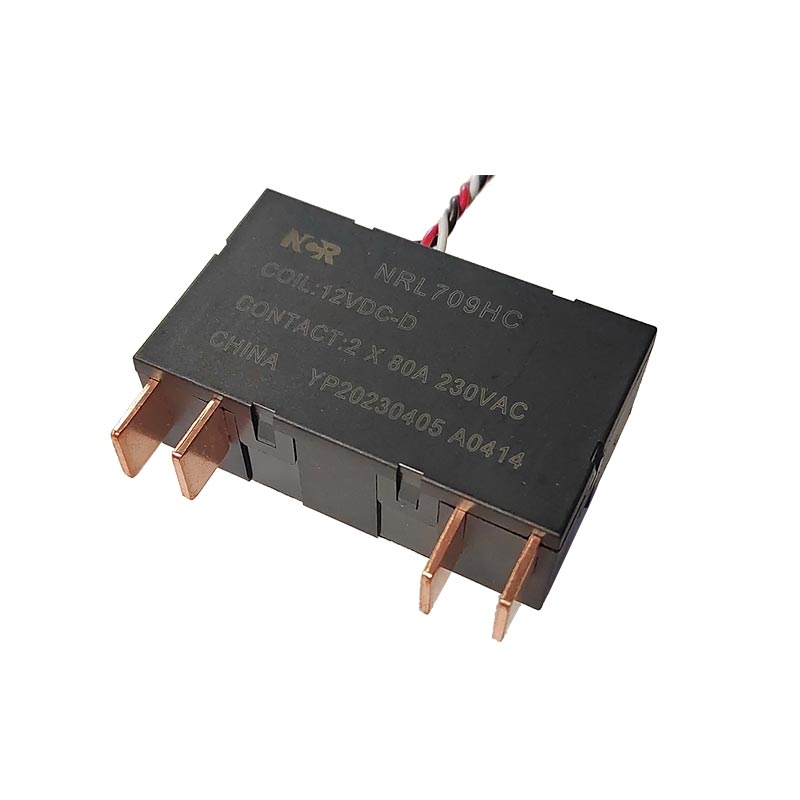
The core components of a relay are the electromagnetic coil and the contacts. The electromagnetic coil, made of wound wires, generates a magnetic field when current flows through it, causing the contacts to close or open. The relay has control and output terminals; applying or cutting off power to the control terminal can control the state of the output terminal.
When power is applied to the control terminal, current flows through the electromagnetic coil, causing the iron core to be attracted by the magnetic field. As the iron core is attracted, the contacts close, forming a path between the output terminals, allowing current to flow.
When power is cut off from the control terminal, the magnetic field in the electromagnetic coil dissipates, causing the iron core to lose its magnetism. The contacts then open due to the action of the return spring, breaking the path between the output terminals, and current stops flowing.
Relays can be classified into normally closed contacts and normally open contacts based on the type of contacts.
Normally Closed Contacts: When the relay is in the inactive state, the contacts are closed, and the circuit is complete. When power is applied to the control terminal, the contacts open, breaking the circuit. This is the most common type of relay.
Normally Open Contacts: When the relay is in the inactive state, the contacts are open, and the circuit is open. When power is applied to the control terminal, the contacts close, completing the circuit. This type of relay is used in specific applications.
Relays can be classified into electromagnetic relays and solid-state relays based on their operating principles.
Electromagnetic Relays: They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, with contacts being closed or opened by the attraction of the iron core and the action of a spring. Because of the mechanical connection of the contacts in electromagnetic relays, they can withstand large currents and are widely used.
Solid-State Relays: They utilize the characteristics of semiconductor materials for control and use optoelectronic isolation to achieve output. Solid-state relays have no mechanical parts, are durable, and their contacts are less susceptible to vibration and corrosion. However, their load capacity is relatively small, mainly suitable for low-power control.
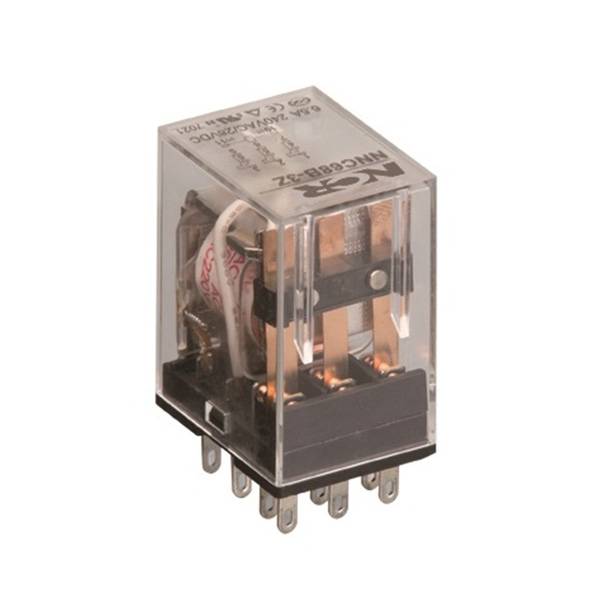

Relays operate in single-pole and double-pole modes.
Single-Pole Relay: The relay has one set of contacts. When power is applied to the control terminal, the contacts close, and the circuit is completed. When power is cut off from the control terminal, the contacts open, and the circuit is broken. This type of relay is commonly used for normal switch circuit control, such as household lighting.
Double-Pole Relay: The relay has two sets of contacts, typically one normally open and one normally closed. When power is applied to the control terminal, the normally open contacts close, and the normally closed contacts open, completing the circuit. When power is cut off from the control terminal, the normally open contacts open, and the normally closed contacts close, breaking the circuit. This type of relay is used for circuits requiring dual control, such as automotive lighting control.
Relays are widely used in various fields such as power, communications, chemical industry, transportation, and medical care. Below are some common applications of relays:
Power Systems: Relays play protective and control roles in power systems, used for overcurrent protection, undervoltage protection, overvoltage protection, seismic protection, etc.
Electrical Control Systems: Relays are used for controlling motors, such as starting and stopping elevators, fans, pumps, etc.
Communication Equipment: Relays are used in communication for switching power supplies, repeaters, circuit switching, etc.
Subway Systems: Relays control signal lights, station door opening and closing, etc., in subway systems.
Household Appliances: Relays are commonly used to control lights, air conditioners, televisions, washing machines, etc., in household appliances.
In conclusion, relays act as electronic switches in circuits, controlling the operation of large currents with small currents and achieving control and protection of the circuit. Relays have various classifications, operating modes, and applications in different fields, but they all operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Relays play an important role in modern electrical control systems, promoting the safe and stable operation of power systems and improving the convenience of production and life.